Normal to the Curve
A line normal to a curve at a given point is the line perpendicular to the line thats tangent at that same point. Solve the following problems.
M414 Chapter 3 Worksheet.
. Find the points of perpendicularity for all normal lines to the. The continuous uniform distribution is a family of symmetric probability distributions in which all intervals of the same length are equally probable. The normally distributed curve should be.
Free normal line calculator - find the equation of a normal line given a point or the intercept step-by-step. 18 Pics about Label a Normal Curve Assessment for 9th - 12th Grade Lesson Planet. The total area under the curve should be equal to 1.
In this definition π is the ratio of the circumference of a circle to its diameter 314159265 and e is the base of the natural. Label a Normal Curve Assessment for 9th - 12th Grade Lesson Planet. Find the gradient of the normal to the curve at P a b.
The normals gradient m is the negative reciprocal of the gradient of the curve at the point P a b thats. Calculate the slope of the tangent to the curve yx 3-x at x2. In a normal distribution the mean median and mode are equal.
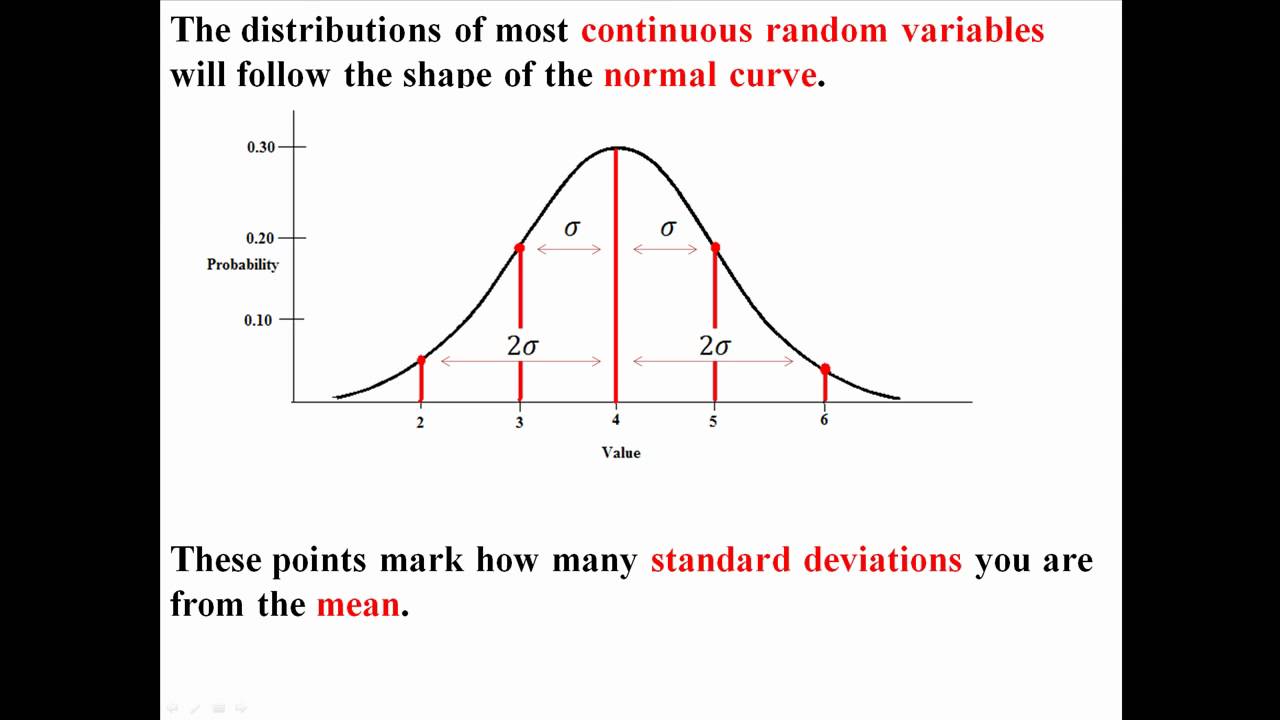
M 1 f a Step. Properties of the Normal Curve. Ie Mean Median Mode.
The normal to the curve is the line perpendicular at right angles to the tangent to the curve at that point. Although in statistics other distributions may be used the normal distribution. We need to differentiate that equation that point dont think too much for.
Therefore the equation of the normal to the curve at 1 1 is y-x 0. The normal curve is sometimes referred to as the bell-shaped curve or the Gaussian curve. Known characteristics of the normal curve make it possible to estimate the probability of occurrence of any value of a normally distributed variable.
Interactive online graphing calculator - graph functions conics and inequalities free of charge. Learning Objectives Contrast sampling from. Standard Normal Distribution Table This is the bell-shaped curve of the Standard Normal Distribution.
It is a Normal Distribution with mean 0 and standard deviation 1. Its equation can be found out by the point-slope form as. Y 2π ½ e x 2 2.
First we need to find given point is on that curve or not if the point is on that curve then. The normal curve has the form.



No comments for "Normal to the Curve"
Post a Comment